The Kremlin has launched a sweeping propaganda campaign to convince young Russians that their country has built the world’s most free and fair elections since President Vladimir Putin came to power, officials have told The Moscow Times.
In an unprecedented move, Russian authorities on Monday held a nationwide school lesson marking the 30th anniversary of the Central Election Commission (CEC)’s creation.
The lesson, which comes six months ahead of the 2024 presidential election that will likely see Putin run for re-election, is the first such effort to engage schoolchildren in politics on a mass scale since the Soviet collapse.
“We’re gradually bringing back the [patriotic] ideology and raising our new generation. If we don’t introduce the right ideology, our enemies will introduce [their own] to our children,” a Russian government official told The Moscow Times on condition of anonymity.
On Monday, election officials led lessons at schools across the country, including in the Baltic exclave of Kaliningrad and the Moscow region town of Lukhovitsy.
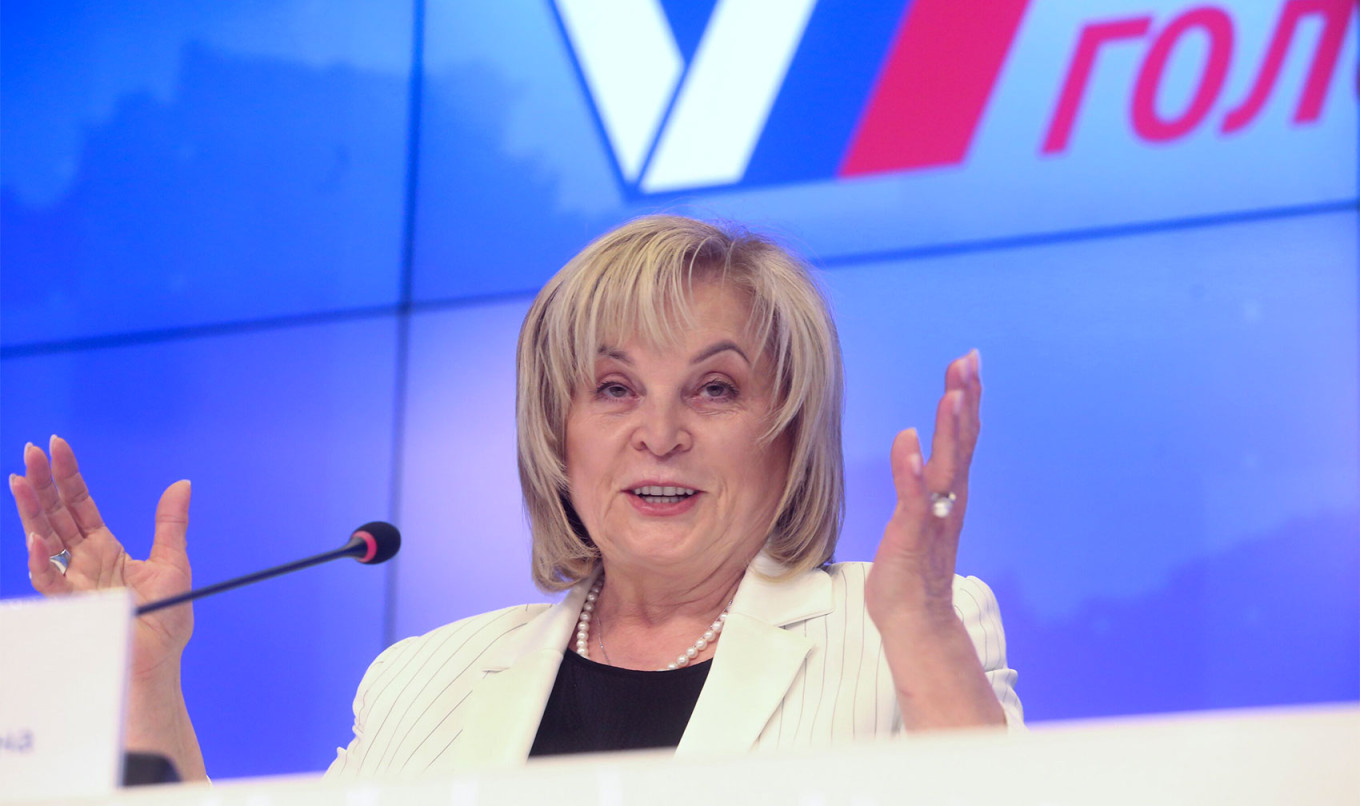
A symbolic component of these lessons was a pre-recorded video address by CEC chief Ella Pamfilova, who called Russia’s elections “the most progressive” and said each election is a meaningful event for every Russian citizen.
In a mock election game, students in lower grades voted for a president among cartoon and fairytale “candidates,” made posters for a polling station and visited kids.kremlin.ru, a children's version of the Kremlin website.
High-schoolers were taught the advantages of the country’s controversial electronic voting system, played a game of voting and vote counting, and were taught "respect for the history of Russia, the values of democracy and the people's choice.”

Young Russians tend to be more involved in activism and protests than older generations, and they are much more likely to oppose the war in Ukraine and Putin’s 23-year regime.
By cultivating faith in the integrity and true democracy of the country's elections, officials aim to boost young people’s confidence in the official election results, a source close to the Kremlin told The Moscow Times.
“And that means [confidence in] the unshakeable authority of the president,” the source said.
The elections-focused lesson was held as part of “Important Conversations,” a new addition to the Russian school curriculum introduced last September after the country’s full-scale assault on Ukraine.
"The point of the lesson is to foster a sense of responsibility and pride for one's country. By forming initial ideas about the electoral right, we educate a citizen who is responsible for the future of his family and his country," the teacher guidelines for “Important Conversations” state.
Democratic processes in Russia have seen a gradual backsliding since Putin took office in 2000, with the elimination of any real competition to his rule, the silencing of independent media and the installation of figurehead “systemic opposition” parties in parliament.
His core support base has traditionally been middle-aged and elderly people, pensioners, state and municipal employees, workers at state-owned companies and women.
“For the past few decades, there was no mass engagement of children in politics. Now, it is happening for a reason — young people have the biggest protest potential,” independent political analyst Abbas Gallyamov, a former speechwriter for Putin, told The Moscow Times.
The Kremlin’s past attempts to boost its support among young people over the past decade have been largely unsuccessful.
At the same time, young people’s sympathy for opposition politicians such as Alexei Navalny became a growing source of concern for the Russian leader.

In 2018, when Putin was seeking a fourth term, many young people in Moscow and St. Petersburg went to rallies organized by supporters of Navalny, who was barred from appearing on the ballot.
More than 1,500 people, many of whom were young adults or even minors, were detained at protests on the day of Putin's 2018 inauguration.
In December of that year the State Duma, at the initiative of the ruling United Russia party, passed a law against the involvement of minors in unauthorized rallies and pickets.
"This is being done to 'slap the hands' of politicians who are trying to use our children for their political purposes," United Russia deputy and former VGTRK deputy chief said Yevgeny Revenko at the time.
Three years later, in March 2021, Putin demanded that police monitor the internet to prevent them from participating in unauthorized street demonstrations — a move that came as thousands of youngsters in many Russian cities were protesting Navalny's arrest.
While Kremlin officials are trying to show Putin that they are educating young people and reducing their likelihood of protesting, Gallyamov said these efforts are a simulation that cannot truly safeguard the regime.
"By teaching children about voting, the Kremlin shows it does not want to cancel elections as a means of determining the people’s will,” said Russian political analyst Ekaterina Kurbangaleeva. “But the term ‘election’ itself is now just a tribute to tradition, with no real competition.”
A Message from The Moscow Times:
Dear readers,
We are facing unprecedented challenges. Russia's Prosecutor General's Office has designated The Moscow Times as an "undesirable" organization, criminalizing our work and putting our staff at risk of prosecution. This follows our earlier unjust labeling as a "foreign agent."
These actions are direct attempts to silence independent journalism in Russia. The authorities claim our work "discredits the decisions of the Russian leadership." We see things differently: we strive to provide accurate, unbiased reporting on Russia.
We, the journalists of The Moscow Times, refuse to be silenced. But to continue our work, we need your help.
Your support, no matter how small, makes a world of difference. If you can, please support us monthly starting from just $2. It's quick to set up, and every contribution makes a significant impact.
By supporting The Moscow Times, you're defending open, independent journalism in the face of repression. Thank you for standing with us.
Remind me later.