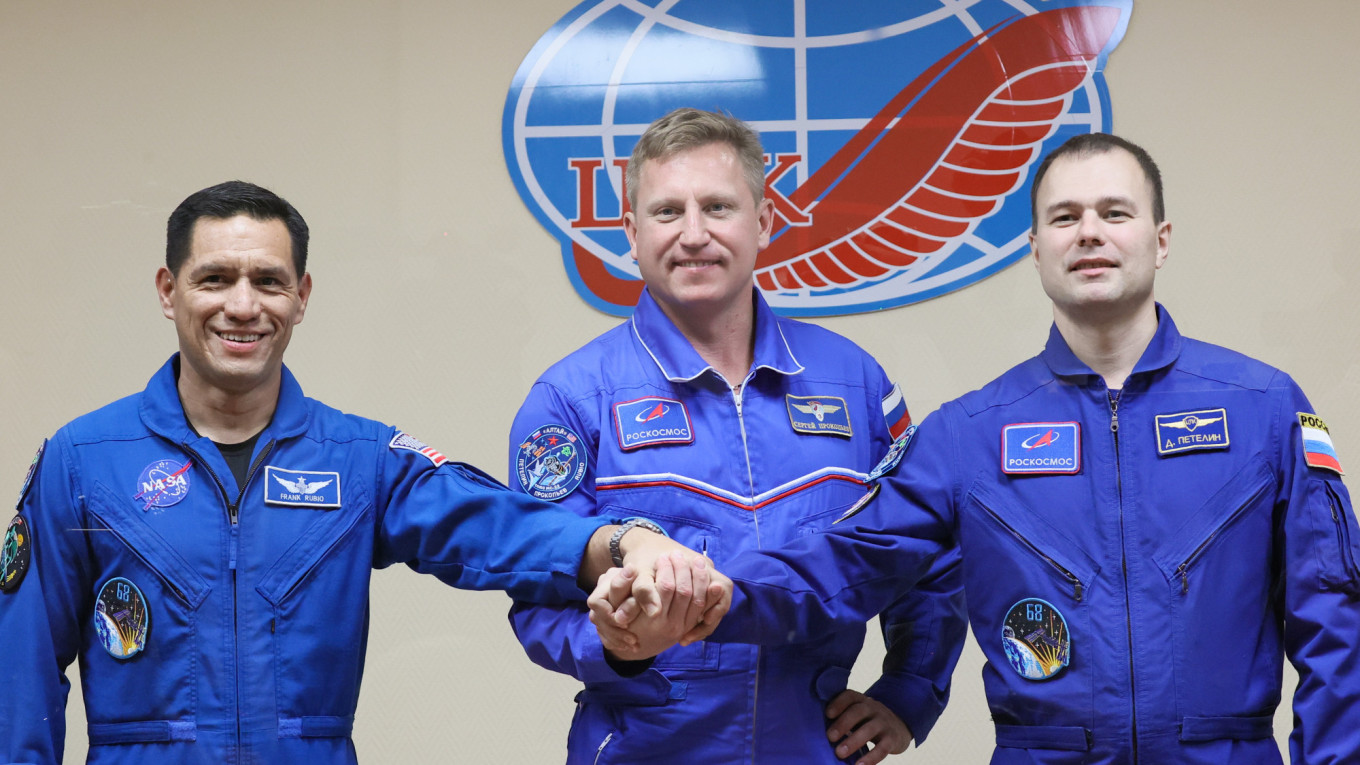
A U.S. astronaut and two Russian cosmonauts are set to blast off to the International Space Station Wednesday on a Russian-operated flight despite soaring tensions between Moscow and Washington over Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
NASA's Frank Rubio and Russia's Sergei Prokopyev and Dmitry Petelin are scheduled to take off from the Russia-leased Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan at 1354 GMT, according to Russian space agency Roscosmos.
Rubio will become the first U.S. astronaut to travel to the ISS on a Russian Soyuz rocket since President Vladimir Putin sent troops into pro-Western Ukraine on Feb. 24.
In response, Western capitals including Washington have hit Moscow with unprecedented sanctions and bilateral ties have sunk to new lows.
However, space has managed to remain an outlier of cooperation between the two countries.
Following Rubio's flight, Russia's only active female cosmonaut Anna Kikina is expected to travel to the orbital station in early October aboard a SpaceX Crew Dragon.
She will become only the fifth professional woman cosmonaut from Russia or the Soviet Union to fly to space, and the first Russian to fly aboard a spacecraft of SpaceX, the company of U.S. billionaire Elon Musk.
With both flights set to go ahead, Russian cosmonauts and Western astronauts have sought to steer clear of the conflict that is raging back on Earth, especially when in orbit together.
A collaboration among the United States, Canada, Japan, the European Space Agency and Russia, the ISS is split into two sections: the U.S. Orbital Segment, and the Russian Orbital Segment.
Russia leaving ISS
At present, the ISS depends on a Russian propulsion system to maintain its orbit, about 250 miles (400 kilometers) above sea level, with the U.S. segment responsible for electricity and life support systems.
However, tensions in the space field have grown after Washington announced sanctions on Moscow's aerospace industry — triggering warnings from Russia's former space chief Dmitry Rogozin, an ardent supporter of the Ukraine war.
Rogozin's recently appointed successor Yuri Borisov later confirmed Russia's long-mooted move to leave the ISS after 2024 in favor of creating its own orbital station.
U.S. space agency NASA called the decision an "unfortunate development" that would hinder the scientific work performed on the ISS.
Space analysts say that the construction of a new orbital station could take more than a decade and Russia's space industry — a point of national pride — would not be able to flourish under heavy sanctions.
The ISS was launched in 1998 at a time of hope for U.S.-Russia cooperation following their Space Race competition during the Cold War.
During that era, the Soviet space program flourished. It boasted a number of accomplishments that included sending the first man into space in 1961 and launching the first satellite four years earlier.
But experts say Roscosmos is now a shadow of its former self and has in recent years suffered a series of setbacks, including corruption scandals and the loss of a number of satellites and other spacecraft.
Russia years-long monopoly on manned flights to the ISS is also gone, to SpaceX, along with millions of dollars in revenue.